
Table of Contents
ToggleAsset Performance Management and 7 Key Maintenance KPIs
Unplanned equipment failures and rising maintenance costs can quietly erode both profitability and trust. Asset Performance Management (APM) addresses these challenges by combining data, analytics, and automation to enhance asset reliability, reduce downtime, and improve decision-making across operations. It transforms maintenance from a reactive cost center into a predictive, performance-driven function.
By aligning people, processes, and technology, APM creates a continuous improvement cycle that keeps assets running at peak efficiency. From predictive insights to data-backed maintenance priorities, it empowers organizations to make smarter investments, extend equipment lifespan, and achieve greater operational stability and financial control.
What is Asset Performance Management (APM)?
You manage high-value physical assets like machines, infrastructure, and facilities. Keeping them reliable is critical. Unplanned failures or hidden wear cut into your margins. They also hurt your credibility. Asset Performance Management (APM) helps you track, analyze, and improve those assets—turning risk into opportunity.
In this article, you’ll learn how APM works, what benefits it unlocks, how to build an effective strategy, the role of modern tech, the four levels of analytics, industry context, and key maintenance KPIs you should track.
What you’ll walk away with:
- The real advantages APM delivers to operations
- An actionable roadmap for APM implementation
- A deep dive into descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics
- Seven essential KPIs to govern asset health
Key Benefits of Asset Performance Management Software
With APM software, you gain visibility, control, and foresight across your asset base. A few core benefits include the following:
- Slash unplanned downtime by predicting failures before they occur.
- Reduce maintenance costs through targeted interventions, rather than over-maintenance.
- Boost asset availability and throughput by ensuring optimal performance.
- Gain operational insight and decision support via analytics dashboards.
- Extend asset lifespan and maximize ROI, deferring capital expenses.
These benefits align with C-level priorities: lower costs, more uptime, predictable operations, and better capital efficiency.
Implementing An Effective APM Strategy
You can’t just flip a switch and expect APM to yield results. You need a structured rollout:
- Define objectives and KPIs up front. Know exactly what success looks like (e.g. 20 % fewer breakdowns, 10 % cost savings).
- Inventory and prioritize assets. Focus on your most critical, highest-risk, highest-impact machines first.
- Install sensors and instrumentation. Use IoT, vibration, thermal, and pressure sensors to feed data.
- Integrate with your existing systems. Tie APM into ERP, EAM, CMMS, SCADA, and data historians.
- Develop analytics models. Start with anomaly detection, then evolve into predictive and prescriptive models.
- Deploy workflows and alerts. Trigger maintenance tasks or inspections based on analytic insights.
- Train teams and iterate. Engineers, operators, and maintenance staff must adopt the system, adjust thresholds, and refine models over time.
Establish continuous feedback loops to allow your APM strategy to progress as assets age and operations shift.
The Role of Technology in Asset Performance Management
Technology underpins APM. Without an advanced stack, you’re just running spreadsheets. Key components include:
- IoT / Industrial sensors to capture real-time data (vibration, temp, pressure)
- Edge computing to preprocess and filter signals near the source
- Data centers/ warehouses to centralize and long-term store sensor data
- Machine learning & AI models for anomaly detection, prognostics, and recommendations
- Visualization and alerting dashboards to translate analytics into decisions
- API layers and integration that connect APM to ERP, CMMS, EAM
Leading APM vendors embed these layers, so you don’t reassemble them yourself.
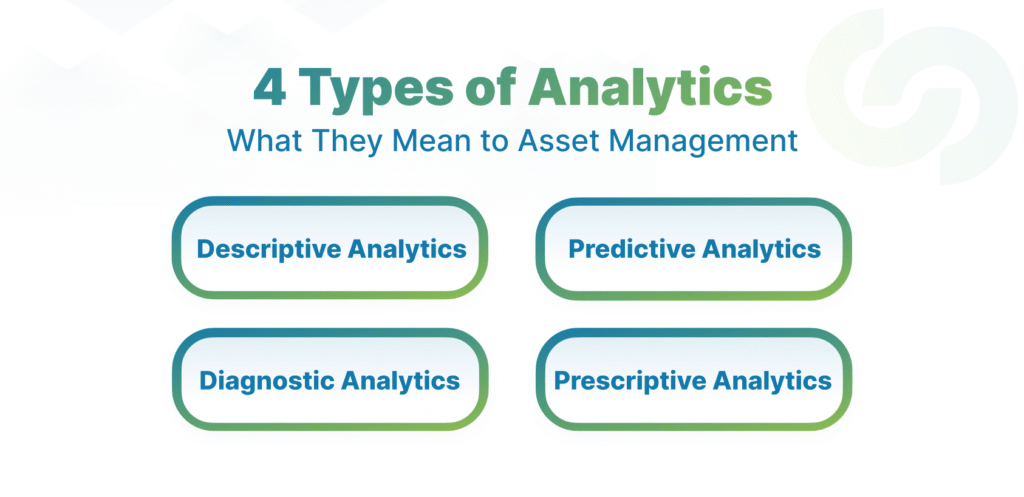
Four Types of Analytics and What They Mean to Asset Management
Analytics is your power lever. You’ll evolve through these four levels:
1. Descriptive Analytics
This shows what happened. You get summaries of downtime, failure counts, maintenance spend, and baseline trends.
2. Diagnostic Analytics
This explains why it happened. You correlate signals, fault logs, and conditions to reveal root causes.
3. Predictive Analytics
This forecasts what will likely happen next. You detect early signs of deterioration and schedule interventions preemptively.
4. Prescriptive Analytics
This recommends what you should do. It can suggest maintenance windows, resource allocation, or replacement timing.
You move from “reporting outcomes” to “automated decision guidance.”
Industry Overview
APM is especially vital in sectors with costly, mission-critical assets: energy, utilities, petrochemical, aviation, mining, and heavy manufacturing. Many of these sectors already operate under regulatory pressures and high availability demands.
The global APM market is expanding rapidly. Some estimates for adjacent domains like application performance show multi-billion-dollar growth, but asset performance domains also mirror that momentum. (Mordor Intelligence+2Grand View Research+2 )
Utility, energy, and industrial firms lead adoption because downtime, compliance, and safety stakes are high. In many regulated industries, APM shifts from optional to mandatory.
Take Control of Your Assets
Unified platform can help you manage and scale your business.
- Centralized Management
- Improved Data Quality
- Future-Proof Your Business
7 Asset Maintenance KPIs You Should Be Tracking and Managing
These KPIs aren’t just numbers for engineers — they are leadership tools. They tell you whether your capital assets are contributing to profitability or quietly draining resources. When you monitor them consistently, you can align technical teams with financial and operational goals.
1. Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)
Calculation:
The formula for MTBF is:
What this means:
MTBF shows how long an asset runs before it breaks down. A higher MTBF means more reliability and less disruption. For executives, MTBF reveals how predictable your operations are. If MTBF is low, you’re burning budget on constant fixes, and downtime is hurting output.
Example:
In manufacturing, a bottleneck machine with a low MTBF could delay entire production lines, costing millions in lost output.
2. Mean Time To Repair (MTTR)
Calculation:
The formula for MTTR is:
MTTR = Total Repair Time / Number of Repairs
What this means:
MTTR measures how long it takes to fix equipment once it fails. Lower MTTR means faster recovery, reduced downtime, and higher productivity. It also reflects the efficiency of your maintenance team and the availability of spare parts.
Example:
If your IT servers have a high MTTR, customer-facing systems could remain offline longer, damaging brand reputation and client trust.
3. Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
Calculation:
- Availability: How often the asset is running versus planned
- Performance: How fast it runs compared to its ideal speed
- Quality: How much output meets standards without defects
OEE is a comprehensive measure of asset utilization. A high OEE shows your assets are producing maximum value. A low OEE pinpoints hidden losses — from idle time to slow performance to rework.
Example:
A plant running at 60% OEE is effectively losing 40% of potential production capacity.
Configurable Equipment Maintenance Software
While not a KPI itself, your APM or CMMS system must allow configuration. Without configurable dashboards and thresholds, you can’t adapt KPIs to your business reality. Executives should demand systems that evolve with strategy, not static metrics that ignore shifting priorities.
4. Cost of Asset Maintenance
Calculation:
5. Cost to Replace vs. Cost to Repair
Calculation:
Compare lifetime repair costs against asset replacement cost.
What this means:
At some point, keeping an old asset alive becomes costlier than replacing it. This KPI helps leaders make capital budgeting decisions based on evidence, not gut instinct.
Example:
If you’ve spent $200,000 repairing a generator that costs $250,000 new, replacement is the financially rational decision.
6. Unplanned Maintenance Percentage
Calculation:
7. Work Order Resolution Time
Calculation:
Time between work order creation and closure (measured in hours or days).
What this means:
This KPI tracks how quickly your team closes maintenance tasks. Faster resolution keeps assets online and boosts operational resilience. It also reflects team productivity, communication efficiency, and process maturity.
Example:
In aviation, long work order resolution times can ground aircraft, disrupt schedules, and increase regulatory risks.
How Integrow’s Unified ERP and CRM Help You Get More from Asset Performance Management
Keeping track of assets, maintenance, and performance across different systems can get messy fast. Integrow brings everything together with your ERP, CRM, and operations into one connected platform. That means you can see how every asset impacts your business, from reliability and costs to customer commitments and ROI.
Here’s how Integrow makes APM simpler and smarter:
- One source of truth: All your assets, maintenance logs, and financials live in one place that is easy to find and easy to trust.
- Smarter maintenance: Built-in AI and analytics predict issues before they happen, helping you plan fixes instead of firefighting.
- Seamless workflows: Maintenance tasks, purchase orders, and approvals all flow through the same system, cutting delays and manual work.
- Clear performance insights: Real-time dashboards show key KPIs like MTBF, MTTR, and OEE so you can make fast, confident decisions.
- Better planning: Align maintenance schedules with available staff, spare parts, and vendor timelines, no surprises, no chaos.
- Flexible by design: Integrow adapts to your business processes, not the other way around.
With everything connected, your teams spend less time switching systems and more time keeping assets performing their best. It’s a smarter, more unified way to manage reliability, cost, and performance all from one platform.
Take Control of Your Assets
Unified platform can help you manage and scale your business.
- Centralized Management
- Improved Data Quality
- Future-Proof Your Business


